TI/Programowanie dla Fizyków Medycznych/Morfologia matematyczna: Różnice pomiędzy wersjami
Z Brain-wiki
| Linia 6: | Linia 6: | ||
a[30:50,30:50]=True | a[30:50,30:50]=True | ||
a[50:70,50:70]=True | a[50:70,50:70]=True | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | brush7=np.array([[0,0,1,1,1,0,0],[0,1,1,1,1,1,0],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[0,1,1,1,1,1,0],[0,0,1,1,1,0,0]],dtype=np.bool) | ||
| + | py.imshow(a, cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest') | ||
| + | py.show() | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | [[Plik:morfologia1.png]] | ||
| − | + | Przydatna będzie procedura | |
| − | + | <source lang="python"> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
def brush2list(brush): | def brush2list(brush): | ||
result=[] | result=[] | ||
| Linia 26: | Linia 24: | ||
if brush[x,y]: result.append((x-middle,y-middle)) | if brush[x,y]: result.append((x-middle,y-middle)) | ||
return result | return result | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| − | def | + | ===Dylacja=== |
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
| + | def dylacja(fig,brush=np.array([[0,1,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,0]],dtype=np.bool)): | ||
result=np.zeros(fig.shape) | result=np.zeros(fig.shape) | ||
brush_list=brush2list(brush) | brush_list=brush2list(brush) | ||
for x in range(3,fig.shape[0]-3): | for x in range(3,fig.shape[0]-3): | ||
for y in range (3,fig.shape[1]-3): | for y in range (3,fig.shape[1]-3): | ||
| − | result[x,y]= | + | result[x,y]=max([fig[x+x_shift,y+y_shift] for (x_shift,y_shift) in brush_list]) |
return result | return result | ||
| + | py.imshow(dylacja(a,brush7), cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest') | ||
| + | py.show() | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| − | + | [[Plik:morfologia-dylacja.png]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ===Erozja=== | ||
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
def erozja(fig,brush=np.array([[0,1,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,0]],dtype=np.bool)): | def erozja(fig,brush=np.array([[0,1,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,0]],dtype=np.bool)): | ||
result=np.zeros(fig.shape) | result=np.zeros(fig.shape) | ||
| Linia 52: | Linia 52: | ||
return result | return result | ||
| + | py.imshow(erozja(a,brush7), cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest') | ||
| + | py.show() | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Plik:morfologia-erozja.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Otwarcie i zamknięcie=== | ||
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
def otwarcie(fig,brush=np.array([[0,1,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,0]],dtype=np.bool)): | def otwarcie(fig,brush=np.array([[0,1,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,0]],dtype=np.bool)): | ||
return dylacja(erozja(fig,brush),brush) | return dylacja(erozja(fig,brush),brush) | ||
| Linia 57: | Linia 65: | ||
def zamkniecie(fig,brush=np.array([[0,1,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,0]],dtype=np.bool)): | def zamkniecie(fig,brush=np.array([[0,1,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,0]],dtype=np.bool)): | ||
return erozja(dylacja(fig,brush),brush) | return erozja(dylacja(fig,brush),brush) | ||
| + | |||
| + | py.imshow(otwarcie(a,brush7), cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest') | ||
| + | py.show() | ||
| + | py.imshow(zamkniecie(a,brush7), cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest') | ||
| + | py.show() | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Plik:morfologia-otwarcie.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Plik:morfologia-zakmniecie.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Filtr medianowy=== | ||
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
| + | def medianowy(fig,brush=np.array([[0,1,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,0]],dtype=np.bool)): | ||
| + | result=np.zeros(fig.shape) | ||
| + | brush_list=brush2list(brush) | ||
| + | for x in range(3,fig.shape[0]-3): | ||
| + | for y in range (3,fig.shape[1]-3): | ||
| + | result[x,y]=np.median([fig[x+x_shift,y+y_shift] for (x_shift,y_shift) in brush_list]) | ||
| + | return result | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | Służy do usuwania szumu. | ||
| + | <source lang="python"> | ||
| + | for x,y in np.ndindex(a.shape): | ||
| + | if (np.random.random()<0.05): a[x,y]=False | ||
| + | if (np.random.random()>0.95): a[x,y]=True | ||
| − | py.imshow(a, cmap= | + | py.imshow(a, cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest') |
py.show() | py.show() | ||
| − | py.imshow | + | a=medianowy(a) |
| + | py.imshow(a, cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest') | ||
py.show() | py.show() | ||
| − | py.imshow | + | a=medianowy(a) |
| + | py.imshow(a, cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest') | ||
py.show() | py.show() | ||
| − | py.imshow | + | a=medianowy(a) |
| + | py.imshow(a, cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest') | ||
py.show() | py.show() | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Plik:morfologia-zaszumiony1.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Plik:morfologia-zaszumiony2.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Plik:morfologia-zaszumiony3.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Plik:morfologia-zaszumiony4.png]] | ||
[["Programowanie dla Fizyków Medycznych"]] | [["Programowanie dla Fizyków Medycznych"]] | ||
Wersja z 23:04, 8 cze 2015
Spis treści
Morfologia Matematyczna
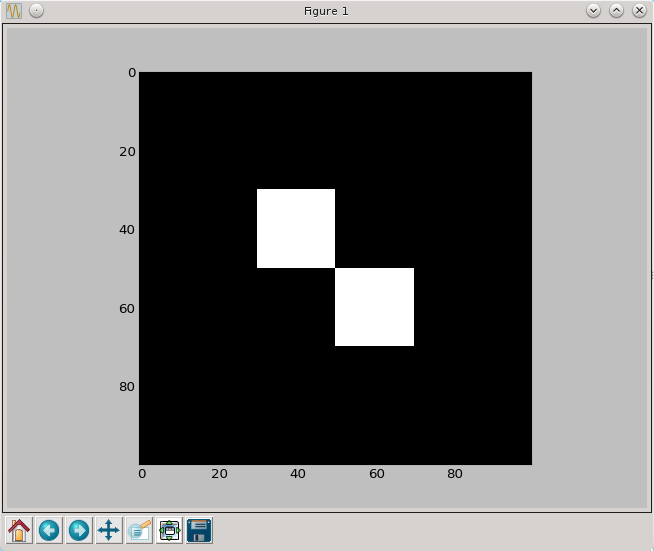
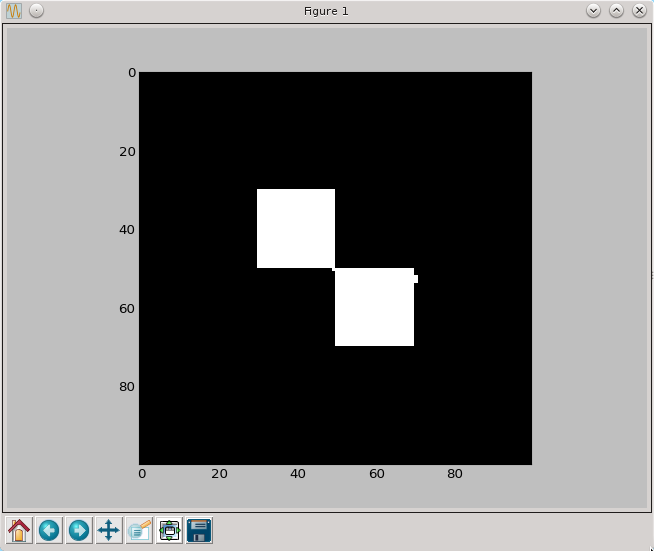
import numpy as np
import pylab as py
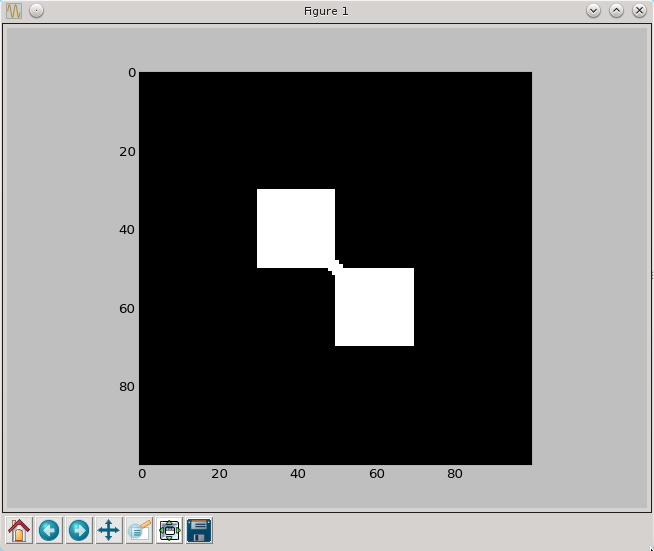
a=np.zeros((100,100),dtype=np.bool)
a[30:50,30:50]=True
a[50:70,50:70]=True
brush7=np.array([[0,0,1,1,1,0,0],[0,1,1,1,1,1,0],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[0,1,1,1,1,1,0],[0,0,1,1,1,0,0]],dtype=np.bool)
py.imshow(a, cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest')
py.show()
Przydatna będzie procedura
def brush2list(brush):
result=[]
N=brush.shape[0]
middle=N/2
for x in range(N):
for y in range(N):
if brush[x,y]: result.append((x-middle,y-middle))
return result
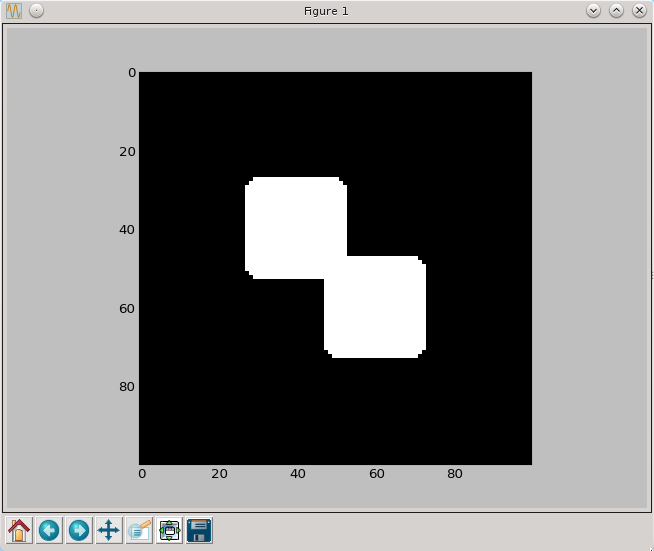
Dylacja
def dylacja(fig,brush=np.array([[0,1,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,0]],dtype=np.bool)):
result=np.zeros(fig.shape)
brush_list=brush2list(brush)
for x in range(3,fig.shape[0]-3):
for y in range (3,fig.shape[1]-3):
result[x,y]=max([fig[x+x_shift,y+y_shift] for (x_shift,y_shift) in brush_list])
return result
py.imshow(dylacja(a,brush7), cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest')
py.show()
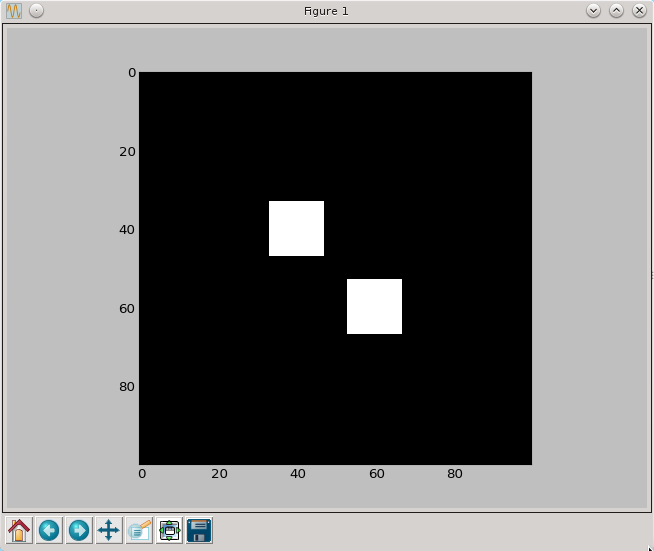
Erozja
def erozja(fig,brush=np.array([[0,1,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,0]],dtype=np.bool)):
result=np.zeros(fig.shape)
brush_list=brush2list(brush)
for x in range(3,fig.shape[0]-3):
for y in range (3,fig.shape[1]-3):
result[x,y]=min([fig[x+x_shift,y+y_shift] for (x_shift,y_shift) in brush_list])
return result
py.imshow(erozja(a,brush7), cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest')
py.show()
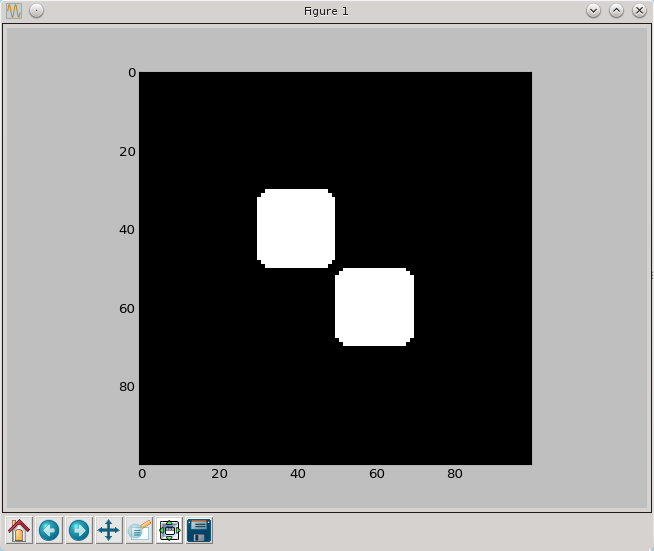
Otwarcie i zamknięcie
def otwarcie(fig,brush=np.array([[0,1,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,0]],dtype=np.bool)):
return dylacja(erozja(fig,brush),brush)
def zamkniecie(fig,brush=np.array([[0,1,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,0]],dtype=np.bool)):
return erozja(dylacja(fig,brush),brush)
py.imshow(otwarcie(a,brush7), cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest')
py.show()
py.imshow(zamkniecie(a,brush7), cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest')
py.show()
Filtr medianowy=
def medianowy(fig,brush=np.array([[0,1,0],[1,1,1],[0,1,0]],dtype=np.bool)):
result=np.zeros(fig.shape)
brush_list=brush2list(brush)
for x in range(3,fig.shape[0]-3):
for y in range (3,fig.shape[1]-3):
result[x,y]=np.median([fig[x+x_shift,y+y_shift] for (x_shift,y_shift) in brush_list])
return result
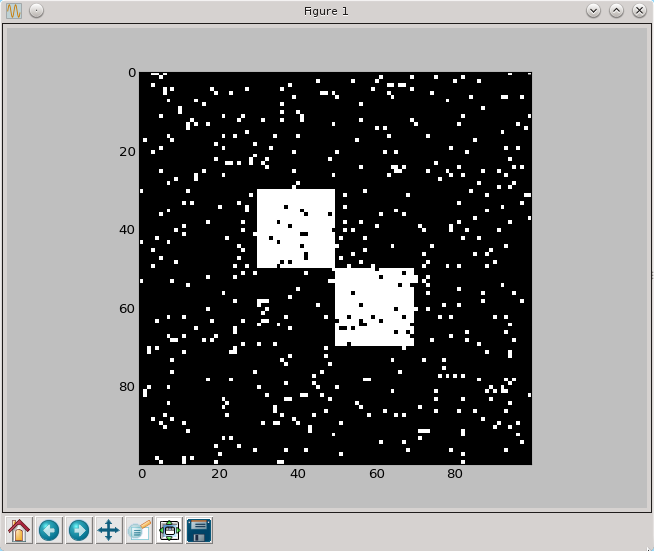
Służy do usuwania szumu.
for x,y in np.ndindex(a.shape):
if (np.random.random()<0.05): a[x,y]=False
if (np.random.random()>0.95): a[x,y]=True
py.imshow(a, cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest')
py.show()
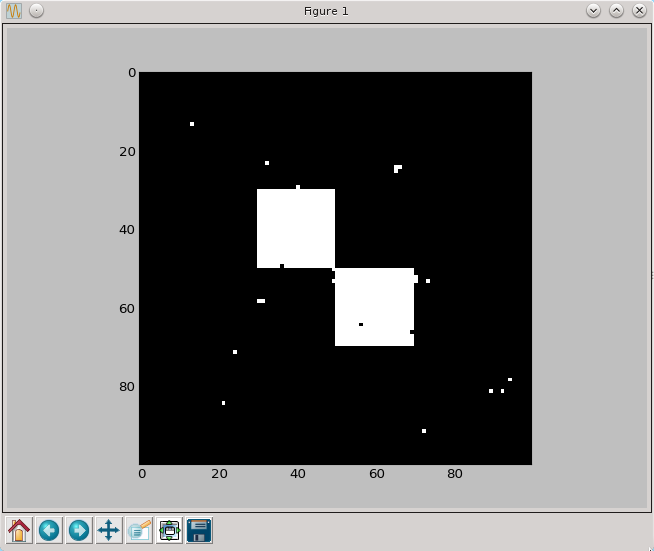
a=medianowy(a)
py.imshow(a, cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest')
py.show()
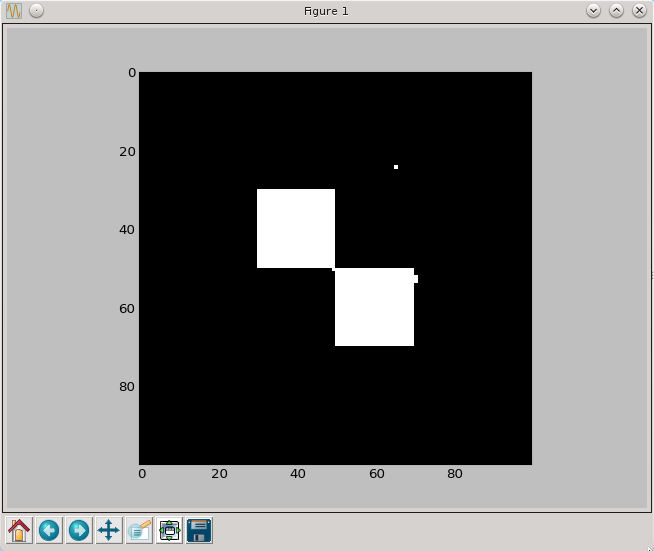
a=medianowy(a)
py.imshow(a, cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest')
py.show()
a=medianowy(a)
py.imshow(a, cmap=py.cm.gray, interpolation='nearest')
py.show()